Material Information
This category focuses on gathering data related to walls, windows, HVAC systems, and thermal insulation.
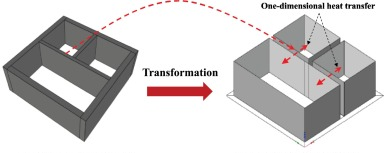
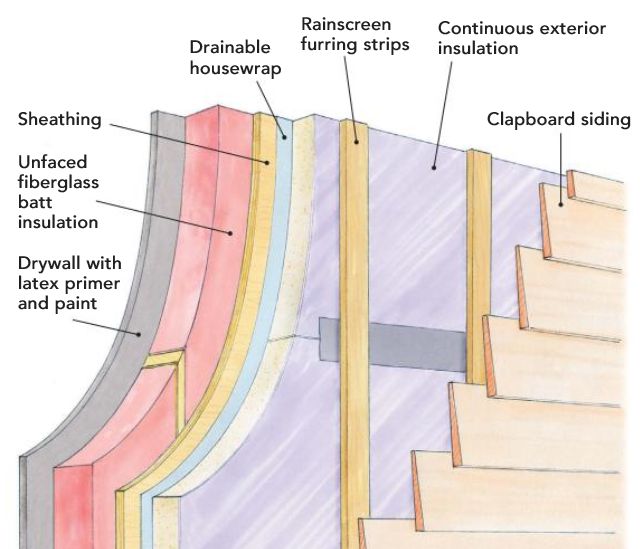
The thermal resistance value of the wall represents the assembly's ability to resist heat transfer between
the interior and exterior environments. For windows, the heat transfer coefficient (U-value) measures the
rate of heat transmission through the window assembly, while the solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC) indicates
the fraction of incident solar radiation that passes through the assembly. Additionally, the thermal conductivity
of the selected insulation material is required. Lastly, the coefficient of performance (COP) of the HVAC system
is needed to convert thermal loads into energy usage.
The material information is categorized into six key data points:
-
R_wall: The R-value measures a material's thermal resistance, expressed in units of m²K/W.
This value refers to the thermal resistance of the external wall.
-
U_glass: The U-value represents the heat transfer rate through a material, expressed in units of W/m²K.
This value refers to the thermal transmittance of the entire window assembly.
-
SHGC: The solar heat gain coefficient measures the fraction of solar radiation passing through a window via reflection,
absorption, and transmittance. The SHGC rating ranges between 0 and 1, representing the performance of the entire
window assembly.
-
λ_insulation: The λ-value measures a material's thermal conductivity, expressed in units of W/mK.
This value refers to the thermal conductivity of the insulation material.
-
COP cooling: The coefficient of performance (COP) represents the ratio of cooling power (kW) delivered by the cooling
system to the power (kW) consumed by its compressor. This value indicates the efficiency of the cooling system.
-
COP heating: Similar to COP cooling, this value represents the ratio of heating power (kW) delivered by the heat pump to
the power (kW) supplied to its compressor. This value refers to the heating system's efficiency.